Write Some C++ Code That Will Fi Ll an Array a With 20 Values of Type Int Read in From the Keyboard.
In elementary English, array ways collection. In C++ too, an assortment is a collection of like types of information. eg.- an array of int volition contain only integers, an array of double volition contain only doubles, etc.
Why Assortment?
Suppose we need to store the marks of l students in a class and summate the average marks. Declaring fifty divide variables volition practise the chore but no developer would like to do and then. And hither comes the array in action.
How to declare an array
datatype array_name [ array_size ] ;
For example, have an integer array 'n'.
int due north[vi];
n[ ] is used to denote an array named 'north'.
So, n[half-dozen] means that 'n' is an array of 6 integers. Here, 6 is the size of the array i.east., there are six elements of array 'due north'.
Giving assortment size i.e. 6 is necessary considering the compiler needs to allocate space to that many integers. The compiler determines the size of an array past computing the number of elements of the array.
Hither 'int due north[6]' volition classify space to 6 integers.
We tin can likewise declare an array past some other method.
int n[ ] = { 2,iii,fifteen,8,48,xiii };
In this case, we are declaring and assigning values to the assortment at the same time. Hence, no need to specify the array size because the compiler gets it from { ii,3,xv,8,48,thirteen }.
Post-obit is the pictorial view of the assortment.
0,1,two,3,4 and 5 are the indices. Information technology is like these are the identities of 6 dissimilar elements of the array. Index starts from 0. Then, the starting time chemical element has index 0. We access the elements of an array by writing array_name[index].
Alphabetize of an array starts with 0.
Here,
northward[0] is ii
n[ane] is 3
n[2] is 15
due north[3] is viii
n[4] is 48
north[v] is thirteen
Initializing an array
Past writing int northward[ ]={ 2,4,8 }; , we are initializing the assortment.
But when we declare an array like int n[3]; , we need to assign the values to information technology separately. Because 'int due north[3];' will definitely allocate the space of 3 integers in the retentivity simply there are no integers in that.
To assign values to the array, assign a value to each of the element of the array.
n[0] = 2;
n[ane] = iv;
n[2] = 8;
It is just like nosotros are declaring some variables and then assigning the values to them.
int x,y,z;
x=2;
y=4;
z=8;
Thus, the two means of initializing an array are:
int n[ ]={ 2,4,8 };
and the second method is declaring the array first and then assigning the values to its elements.
int n[3];
north[0] = 2;
n[one] = 4;
n[ii] = 8;
You can understand this past treating n[0], n[1] and n[2] as unlike variables y'all used earlier.
But like a variable, an assortment can be of whatever other data type besides.
float f[ ]= { 1.ane, 1.4, 1.v};
Here, f is an array of floats.
Showtime, let's encounter the example to calculate the average of the marks of three students. Here, marks[0], marks[one] and marks[2] stand for the marks of the outset, 2d and tertiary educatee respectively.
#include <iostream> int main (){ using namespace std ; int marks [ 3 ]; float average ; cout << "Enter marks of first student" << endl ; cin >> marks [ 0 ]; cout << "Enter marks of second student" << endl ; cin >> marks [ 1 ]; cout << "Enter marks of third student" << endl ; cin >> marks [ 2 ]; average = ( marks [ 0 ] + marks [ 1 ] + marks [ 2 ] ) / 3.0 ; cout << "Average marks : " << boilerplate << endl ; render 0 ; }
Enter marks of first pupil
23
Enter marks of second student
25
Enter marks of tertiary student
31
Average marks : 26.3333
Here, you have seen a working example of array. We treated the array in the verbal similar fashion as we had treated normal variables.
In the above case, two points should be kept in mind.
The average value should be of type 'bladder' considering the boilerplate of integers can be bladder also.
Secondly, while taking out the boilerplate, sum of the numbers should be divided by 3.0 and not 3, otherwise, you will go the average value as integer and not float.
Nosotros tin can likewise use for loop as in the next example.
#include <iostream> int chief (){ using namespace std ; int n [ 10 ]; /* declaring n as an array of 10 integers */ int i , j ; /* initializing elements of assortment n */ for ( i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) { cout << "Enter value of n[" << i << "]" << endl ; cin >> n [ i ]; } /* printing the values of elements of assortment */ for ( j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j ++ ) { cout << "northward[" << j << "] = " << due north [ j ] << endl ; } return 0 ; }
Enter value of n[0]
23
Enter value of n[1]
25
Enter value of due north[2]
31
Enter value of n[iii]
i
Enter value of n[4]
33
Enter value of n[5]
35
Enter value of northward[6]
76
Enter value of north[7]
47
Enter value of n[8]
74
Enter value of n[9]
45
due north[0] = 23
n[1] = 25
due north[2] = 31
due north[3] = one
n[iv] = 33
n[five] = 35
n[half-dozen] = 76
north[7] = 47
n[8] = 74
north[9] = 45
The in a higher place code was only to brand you lot familiar with using loops with an array considering you lot volition exist doing this many times subsequently.
The code is simple, i and j starts from 0 because index of an array starts from 0 and goes up to nine ( for x elements ). So, i and j goes upwardly to 9 and not 10 ( i<x and j<x ) . So in the above code, due north[i] volition exist n[0], due north[1], n[ii], ...., northward[ix].
In that location are two for loops in the higher up example. In the start for loop, we are taking the values of the different elements of the array from the user i by one. In the 2nd for loop, we are press the values of the elements of the array.
Permit's become to the commencement for loop. In the showtime iteration, the value of i is 0, then 'n[i]' is 'due north[0]'.Thus past writing cin >> n[i];, the user will be asked to enter the value of n[0]. Similary in the second iteration, the value of 'i' volition be 1 and 'n[i]' will be 'n[i]'. And then 'cin >> due north[i];' will be used to input the value from the user for n[one] and so on. 'i' volition become upward to 9, and so indices of the assortment ( 0,1,ii,...,nine).
Array allocates contiguous memory. Thus if the address of the kickoff chemical element of an assortment of integers is Ten and then the accost of the second element will be X+4 (4 is the size of 1 integer) ) and 3rd will exist X+4+4 and then on. This means that the memories of all elements of an array are allocated together and are continuous.
Arrow to Arrays
Till now, you accept seen how to declare and assign values to an array. Now, you volition see how we can take pointers to arrays too. Simply before starting, we are assuming that you have gone through Pointers. If not, then first read the topic Pointers and do some problems from the Exercise section.
As nosotros all know that pointer is a variable whose value is the address of some other variable i.e., if a variable y points to another variable x ways that the value of the variable 'y' is the address of '10'.
Similarly, if we say that a variable y points to an assortment northward, then it means that the value of 'y' is the address of the offset chemical element of the assortment i.e., n[0]. So, y is the arrow to the array n.
Array proper noun is a pointer to the first element of the array.
If p is a pointer to the array age, then it ways that p(or age) points to age[0].
int age[l];
int *p;
p = age;
The above code assigns the address of the first element of age to p.
Now, since p points to the first element of the array age, *p is the value of the first element of the array.
Since *p refers to the starting time assortment element, *(p+1) and *(p+2) refers to the 2nd and third elements respectively and then on.
So, *p is age[0], *(p+1) is historic period[ane], *(p+two) is age[2].
Similarly, *historic period is historic period[0] ( value at historic period ), *(age+1) is age[1] ( value at historic period+1 ), *(age+2) is age[2] ( value at age+2 ) and so on.
That'due south all in pointer to arrays.
Now allow's see some examples.
#include <iostream> int main (){ bladder n [ 5 ] = { 20.4 , 30.0 , v.8 , 67 , 15.2 }; /* declaring n as an array of 5 floats */ float * p ; /* p every bit a arrow to float */ int i ; p = north ; /* p now points to array due north */ /* printing the values of elements of array */ for ( i = 0 ; i < v ; i ++ ) { std :: cout << "*(p + " << i << ") = " << * ( p + i ) << std :: endl ; /* *(p+i) means value at (p+0),(p+i)...*/ } return 0 ; }
*(p + 0) = twenty.iv
*(p + ane) = thirty
*(p + 2) = 5.8
*(p + three) = 67
*(p + 4) = 15.2
Since p is pointing to the first element of array, and so, *p or *(p+0) represents the value at p[0] or the value at the showtime element of p. Similarly, *(p+i) represents value at p[1]. Then *(p+3) and *(p+4) represent the values at p[iii] and p[4] respectively. And so, accordingly, we volition get the output.
The above example sums upwardly the above concepts. Now, let's print the address of the array and likewise private elements of the array.
#include <iostream> int main (){ int northward [ 4 ] = { xx , thirty , v , 67 }; /* declaring due north as an array of 4 integers */ int * p ; /*a pointer*/ int i ; p = n ; /*p is pointing to array n*/ /* printing the accost of array */ std :: cout << "Accost of array n = " << p << std :: endl ; /*p points to array means store address of first element of array*/ /* printing the addresses of elements of array */ for ( i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++ ) { std :: cout << "Address of n[" << i << "] = " << & n [ i ] << std :: endl ; } return 0 ; }
Accost of array n = 0xfffe2c0c
Accost of due north[0] = 0xfffe2c0c
Address of n[1] = 0xfffe2c10
Address of n[2] = 0xfffe2c14
Accost of north[3] = 0xfffe2c18
In the above example, we saw that the address of the first element of n and p is the same. Nosotros also printed the values of other elements of the array by using (p+one), (p+2) and (p+3).
Passing the whole Assortment in Office
In C++, we tin can pass an element of an array or the full assortment as an statement to a function.
Allow'southward first pass a single assortment element to a function.
#include <iostream> void display ( int a ) { std :: cout << a << std :: endl ; } int chief (){ int due north [ ] = { 20 , xxx , 23 , four , 5 , 2 , 41 , eight }; display ( n [ 2 ]); return 0 ; }
Passing an unabridged Array in a Function
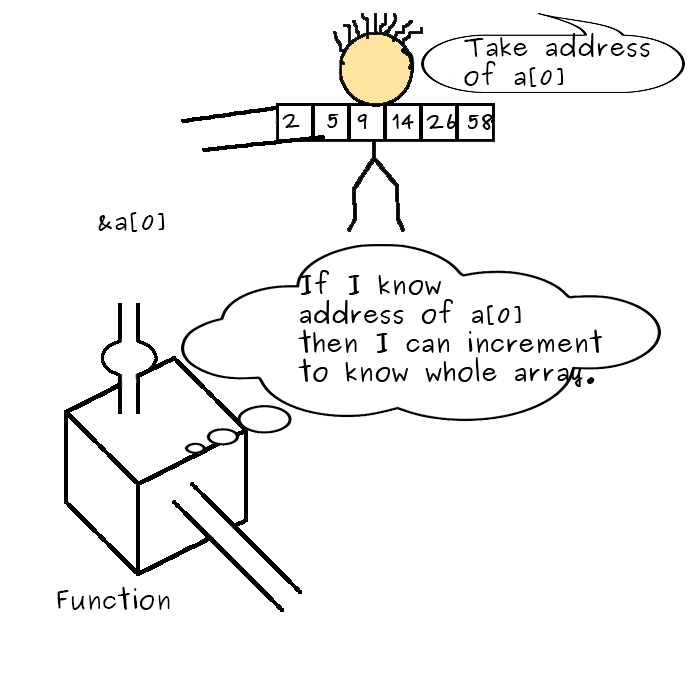
Nosotros tin also pass a whole array to a role by passing the array proper noun equally argument. Yes, the pull a fast one on is that nosotros will pass the address of array, that is the address of the first element of the array. Thus, by having the pointer of the beginning element, nosotros can go the unabridged array as we take done in the higher up examples.
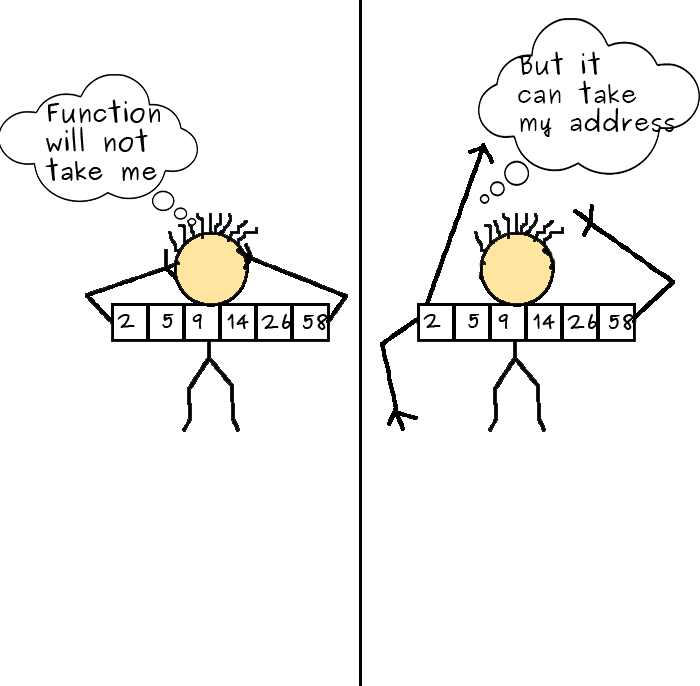
Allow'due south meet an example to sympathize this.
#include <iostream> float average ( bladder a []) { int i ; float avg , sum = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < eight ; ++ i ) { sum += a [ i ]; } avg = sum / viii ; return avg ; } int main (){ float b , n [ ] = { 20.6 , xxx.8 , 5.1 , 67.2 , 23 , ii.ix , 4 , 8 }; b = average ( northward ); std :: cout << "Average of numbers = " << b << std :: endl ; return 0 ; }
Average of numbers = 20.2
average(float a[]) - It is the function that is taking an array of float. And residual of the body of the function is performing accordingly.
b = boilerplate(n) - One affair you should annotation here is that we passed n. And every bit discussed earlier, due north is the pointer to the first chemical element or arrow to the array n[]. So, we have actually passed the arrow.
In the higher up example in which nosotros calculated the average of the values of the elements of an array, nosotros already knew the size of the array i.e., 8.
Suppose, we are taking the size of the assortment from the user. In that case, the size of the array is not fixed. Hither, nosotros need to laissez passer the size of the assortment as the second argument to the function.
#include <iostream> float boilerplate ( bladder a [], int size ) { int i ; bladder avg , sum = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++ ) { sum += a [ i ]; } avg = sum / size ; return avg ; } int main (){ using namespace std ; int size , j ; cout << "Enter the size of array" << endl ; cin >> size ; bladder b , n [ size ]; for ( j = 0 ; j < size ; j ++ ) { cout << "Value of n[" << j << "] : " << endl ; cin >> n [ j ]; } b = average ( n , size ); cout << "Boilerplate of numbers= " << b << endl ; return 0 ; }
Enter the size of array
4
Value of n[0] :
47
Value of n[one] :
74
Value of n[2] :
45
Value of n[three] :
56
Average of numbers= 55.5
The lawmaking is similar to the previous one except that nosotros passed the size of array explicitly - bladder average(float a[], int size).
Nosotros tin also pass an assortment to a part using pointers. Let'due south encounter how.
#include <iostream> using namespace std ; void brandish ( int * p ) { int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++ i ) { cout << "northward[" << i << "] = " << * p << endl ; p ++ ; } } int main (){ int size , j ; int northward [ ] = { one , ii , iii , 4 , 5 , six , 7 , 8 }; display ( n ); return 0 ; }
north[0] = one
n[one] = 2
n[2] = 3
n[3] = 4
due north[4] = v
due north[5] = 6
n[vi] = 7
n[seven] = 8
In the above instance, the address of the array i.eastward., accost of n[0] is passed to the formal parameters of the function.
void display(int *p) - This means that the office 'display' is taking a arrow of an integer and not returning any value.
At present, we passed the arrow of an integer i.due east., pointer of assortment n[] - 'due north' as per the need of our office 'brandish'.
Since p is the accost of the assortment due north[] in the function 'display', i.eastward., the address of the first element of the array (n[0]), therefore *p represents the value of n[0]. In the for loop in the function, p++ increases the value of p by 1. And so when i=0, the value of *p gets printed. Then p++ increases *p to *(p+1) and thus in the second loop, the value of *(p+1) i.e. northward[ane] gets printed. This loop continues till i=7 when the value of *(p+7) i.eastward. n[vii] gets printed.
For-each loop
In that location is a new form of for loop which makes iterating over arrays easier. Information technology is chosen for-each loop. It is used to iterate over an array. Allow's see an instance of this.
#include <iostream> int primary () { using namespace std ; int ar [] = { ane , 2 , 3 , four , five , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 }; for ( int yard : ar ) { cout << thousand << endl ; } return 0 ; }
This is very simple. Here, the variable thou will go to every chemical element of the array ar and will have its value.
And then, in the first iteration, chiliad is the onest element of array ar i.e. 1.
In second iteration, it is the 2nd element i.e. 2 and then on. Simply focus on the syntax of this for loop, rest of the part is very easy.
2nd Arrays
What if arrays are 2 dimensional?
Yes, ii-dimensional arrays also exist and are generally known as matrix. These consist of rows and columns.
Before going into its application, allow'due south first encounter how to declare and initialize a 2 D array.
Like to one-dimensional array, we ascertain 2-dimensional array every bit below.
int a[2][4];
Here, a is a 2-D array of blazon int which consists of 2 rows and 4 columns.
It is similar
| Column 0 | Column 1 | Cavalcade 2 | Cavalcade three | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 0 | a[0][0] | a[0][1] | a[0][2] | a[0][three] |
| Row one | a[ane][0] | a[ane][1] | a[one][2] | a[1][iii] |
At present allow's run into how to initialize a ii-dimensional array.
Initialization of ii D Array
Same as in one-dimensional array, nosotros tin can assign values to a 2-dimensional array in 2 means every bit well.
In the commencement method, but assign a value to the elements of the array. If no value is assigned to any element, then its value is assigned zip past default.
Suppose we declared a two-dimensional assortment a[two][2]. And then to assign information technology values, we demand to assign a value to its elements.
int a[2][two];
a[0][0]=i;
a[0][i]=ii;
a[1][0]=3;
a[1][1]=four;
The 2d way is to declare and assign values at the aforementioned time as nosotros did in i-dimensional array.
int a[2][iii] = { one, 2, 3, iv, v, half dozen };
Here, value of a[0][0] is 1, a[0][i] is 2, a[0][2] is iii, a[1][0] is iv, a[ane][1] is 5 and a[ane][ii] is vi.
We can likewise write the higher up code as:
int a[2][3] = {
{i, 2, 3},
{iv, 5, half-dozen }
};
While assigning values to an array at the fourth dimension of announcement, at that place is no need to give dimensions in one-dimensional array, but in ii D array, we need to give at least the second dimension.
Let's consider different cases of initializing an assortment.
int a[2][2] = { 1, ii, 3, iv }; /* valid */
int a[ ][2] = { 1, 2, three, 4 }; /* valid */
int a[2][ ] = { i, 2, three, iv }; /* invalid */
int a[ ][ ] = { i, 2, 3, four }; /* invalid */
Why employ 2 D Array?
Suppose we have 3 students each studying 2 subjects (subject one and bailiwick 2) and we have to display the marks in both the subjects of the 3 students. Let's input the marks from the user.
#include <iostream> using namespace std ; int main (){ float marks [ 3 ][ ii ]; int i , j ; for ( i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) { /* input of marks from the user */ cout << "Enter marks of student " << ( i + 1 ) << endl ; for ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; j ++ ) { cout << "Subject field " << ( j + i ) << endl ; cin >> marks [ i ][ j ]; } } /* printing the marks of students */ for ( i = 0 ; i < iii ; i ++ ) { cout << "Marks of educatee " << ( i + 1 ) << endl ; for ( j = 0 ; j < ii ; j ++ ) { cout << "Subject " << ( j + 1 ) << " : " << marks [ i ][ j ] << endl ; } } return 0 ; }
Enter marks of student ane
Subject 1
78
Discipline 2
94
Enter marks of educatee ii
Discipline 1
87
Subject 2
91
Enter marks of student 3
Subject area one
62
Subject ii
56
Marks of student 1
Subject i : 78
Subject 2 : 94
Marks of student two
Subject i : 87
Field of study 2 : 91
Marks of student iii
Bailiwick one : 62
Subject two : 56
In the above example, firstly we defined our array consisting of 3 rows and two columns every bit float marks[3][2];
Here, the elements of the assortment will incorporate the marks of the iii students in the 2 subjects as follows.
| Subject area 1 | Subject 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Student ane | 78 | 94 |
| Student ii | 87 | 91 |
| Student iii | 62 | 56 |
In our example, firstly we are taking the value of each element of the array using a for loop inside another for loop.
In the first iteration of the outer for loop, value of 'i' is 0. With the value of 'i' as 0, when the inner for loop first iterates, the value of 'j' becomes nada and thus marks[i][j] becomes marks[0][0]. By writing cin >> marks[i][j];, we are taking the value of marks[0][0].
Later on that, the inner for loop again iterates and the value of 'j' becomes 1. marks[i][j] becomes marks[0][1] and its value is taken from the user.
Then, the outer loop iterates for the 2nd time and the value of 'i' becomes 1 and the whole process continues.
After assigning the values to the elements of the array, nosotros are press the values of the elements of the array, in the same way, using another for loop inside for loop.
Let's run across one more than case of ii D Array
Suppose there are 2 factories and each of these factories produces items of four different types similar some items of blazon 1, some items of type 2 and so on. We have to calculate the total product of each factory i.eastward. sum of the items of each blazon that a factory produces.
#include <iostream> using namespace std ; int main (){ int due south [ 2 ][ iv ]; s [ 0 ][ 0 ] = 2 ; south [ 0 ][ 1 ] = five ; s [ 0 ][ 2 ] = 7 ; s [ 0 ][ 3 ] = iv ; southward [ 1 ][ 0 ] = 9 ; south [ 1 ][ i ] = 3 ; s [ 1 ][ 2 ] = 2 ; south [ i ][ 3 ] = 8 ; cout << "Sum of the items produced in the beginning factory :" << endl ; int sum1 = 0 , sum2 = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < four ; i ++ ) { sum1 += s [ 0 ][ i ]; } cout << sum1 << endl ; cout << "Sum of the items produced in the second manufacturing plant :" << endl ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j ++ ) { sum2 += south [ 1 ][ j ]; } cout << sum2 << endl ; return 0 ; }
Sum of the items produced in the first manufacturing plant :
18
Sum of the items produced in the second manufactory :
22
Here, southward[0][i] represents the number of items of the first factory and type i, where i takes value from 0 to three using for loop and s[one][i] represents the nunmber of items of the 2d factory of type i. E.g. - s[0][2] represents the third type of item of first factory and s[1][2] represents the 3rd type of particular of second manufacturing plant. sum1 is the sum of all these items of mill i. Similar is the case of the second manufactory.
So, initally, sum1 is 0. At present in first iteration, s[0][i] is due south[0][0]. This means that it volition represent number of showtime item of starting time factory. And so, sum1 += s[0][i] will become sum1 += s[0][0]. So, sum1 will become 2. Similarly in 2d iteration, south[0][i] will become s[0][one] and will represent the second type of items of first factory. Now, sum1 will go ii+5 i.e. 7. Similarly things will become farther.
To learn from simple videos, you lot tin ever expect at our C++ video course on CodesDope Pro. Information technology has over 750 practice questions and over 200 solved examples.
You lot practise and you lot get better. It's very uncomplicated.
-Phillip Drinking glass
cabreraboxylost1970.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.codesdope.com/cpp-array/
0 Response to "Write Some C++ Code That Will Fi Ll an Array a With 20 Values of Type Int Read in From the Keyboard."
ارسال یک نظر